The solutions to a quadratic Equation is when the Parabola touches the X- axis which are also called the "roots".
The Discriminant is B^2 - 4AC
If B^2 - 4ac > 0 you`ll get two solutions
If B^2 - 4ac = 0 you`ll get one solution
If B^2 - 4ac < 0 you`ll get no solution
For example :
X^2 + 6X + 9 = 0
A = 1 B^2 - 4ac = ?
B = 6 6^2 - 4(1)(9)
C = 9 36 - 36 = 0
(One solution) because its equal to Zero
Another example:
-16x^2 + 11x - 11 = 0
A = -16 B^2 - 4ac =?
B = 11 11^2 - 4(-16)(-11)
C = -11 121-+ 64(-11)
121 + -704
-583
(NO solution) because its less then Zero
Example:
5x^2 + 2x - 10 = 0
A=5 b^2 - 4ac
B=2 2^2 - 4(5)(-10)
C=-10 4- 200
204
( Two solutions) because its greater then Zero
Monday, April 16, 2012
How Do We Work with quadratics?
The first thing that you should think of when you think of quadratics is the
Quadratic Equation:

So if you have the equation x^2 + 2x - 1
A = 1
B = 2
The value of C is the number without an x after it
C = -1
Step 1: plug in
Step 2 : simplify
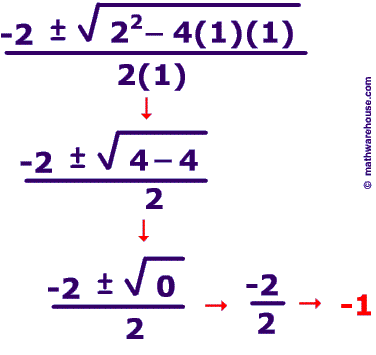
Quadratic Equation:

So if you have the equation x^2 + 2x - 1
- First you have to find the value of A, B and C
- The value of A is in front of the first x
A = 1
- The value of B is in front of the second X
B = 2
The value of C is the number without an x after it
C = -1
Step 1: plug in
Step 2 : simplify
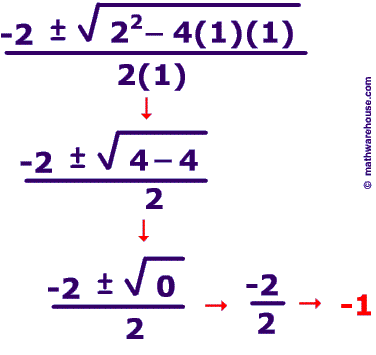
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)